How To Make a Plastic Paint Bucket Mold?
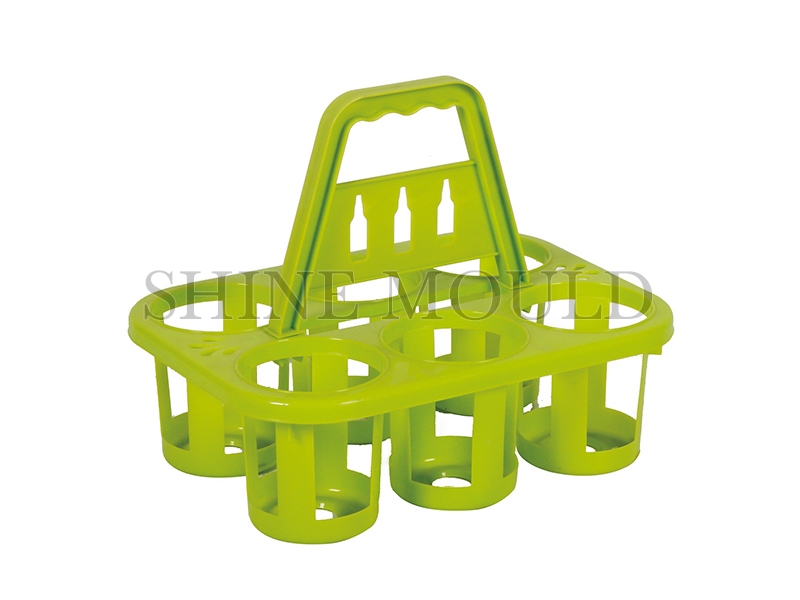
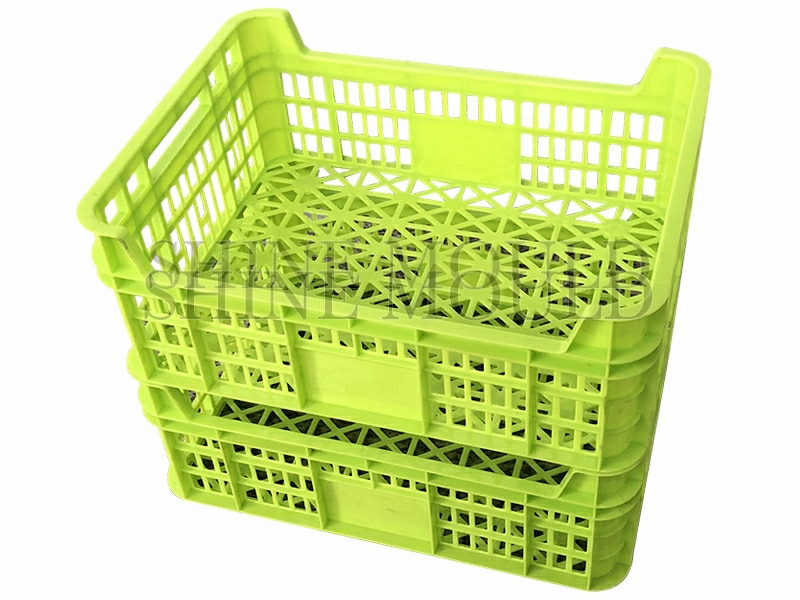
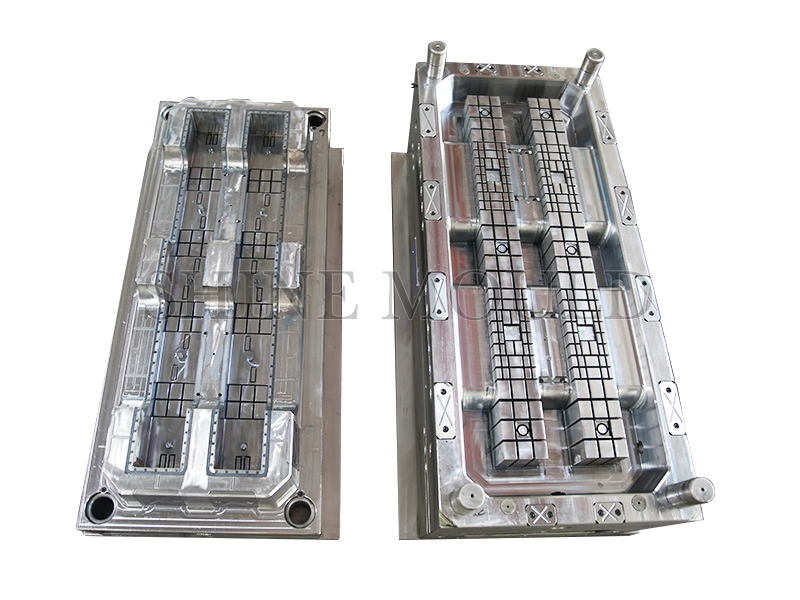
Bucket mold is one of our most important injection molds. Our bucket molds include thin-walled bucket molds, bucket molds, square bucket molds, industrial buckets, and bucket molds, bucket molds, industrial paint bucket molds, packaging bucket molds, garbage Bucket molds, cement bucket mold, plastic bucket mold, and other bucket molds.
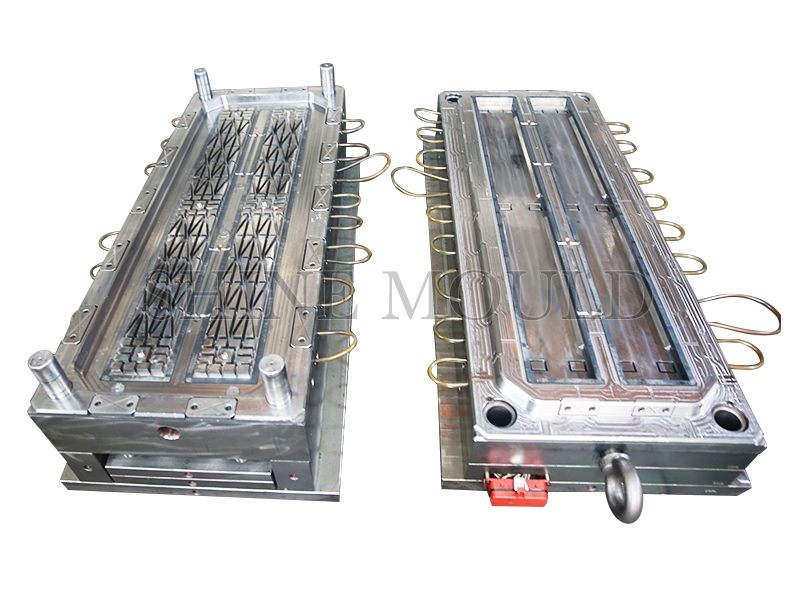
A high-quality Bucket Mould structure is a prerequisite before qualified mold manufacturing. We attach great importance to the analysis of mold structure, including draft angle, product surface microcosm, gate system design, exhaust design, cooling system design, etc. Prone problems will be solved through trial and error in the mold structure design.
In order to improve mold life and product quality, we have improved the hardness of mold steel through heat treatment. In order to prevent mold eccentricity, our commonly used steels are H13, 2316, etc., and we use a whole piece of steel to make buckets. The cooling system is very important. We adopt a single-circuit cooling method and set up evenly distributed water channels as much as possible. Our bucket mold uses air assist, ejector plate, and center ejector for demolding. There are also waterways in the center.
Maintaining mold maintenance is very important. We should check to make sure that the water channel and air circuit are unlocked. Lubricate the muffler and clean the scraper and center ejector regularly. The design of the cooling system is a relatively cumbersome task, that is, the uniformity and cooling effect of the cooling must be considered, and the entire mold structure must also be affected. The exact position and size of the cooling system must be determined; and the cooling of key locations, such as Movable plates or inserts, side sliders, and side cores; standard cooling element design and selection of standard cooling components. SHINE MOULD will analyze a series of factors when starting the mold design. Each part of the mold has circulating water flow, which reduces cooling time, improves production efficiency, and greatly reduces production costs.




 Search...
Search... English
English



.jpg)
