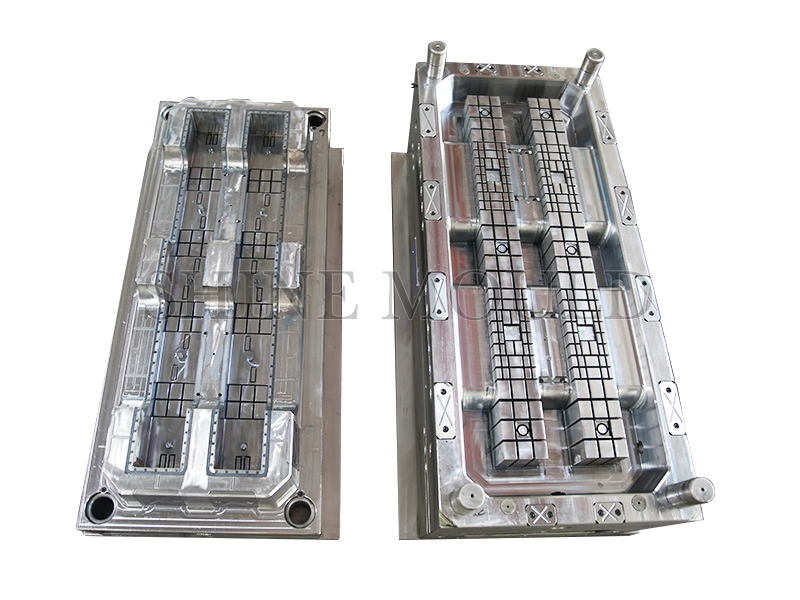
Material Innovation and the Use of Bioplastics in Precision Toy Injection Moulding
The integration of eco-friendly materials in toy manufacturing has prompted a closer examination of the compatibility between conventional mould systems and biodegradable plastics. In particular, the use of Children Toy Mould in conjunction with new materials raises both opportunities and challenges. Traditional thermoplastics like ABS and PP are widely used due to their stable flow properties and predictable cooling behavior, which aligns well with existing mould technologies. However, biodegradable plastics, including PLA, PHA, or starch-based compounds, often behave differently under heat and pressure, prompting an evaluation of how existing moulds can adapt to these emerging substances.

One of the significant considerations lies in thermal behavior. Biodegradable plastics generally have a narrower processing temperature window compared to petroleum-based resins. This means that the tooling used in injection moulding must ensure highly accurate temperature control, as slight deviations could cause degradation, burning, or inconsistent cavity filling. While modern Children's Toy Mould systems are often equipped with advanced temperature management capabilities, retrofitting or fine-tuning older tools may be necessary to meet the thermal demands of biodegradable plastics without compromising part quality.
Another critical factor is the flow characteristics of newer biodegradable resins. These materials often exhibit lower melt strength and may have higher viscosity, which can impact how well the plastic fills intricate details within the mould. Toys, especially those with small mechanical components or decorative features, require moulds capable of handling precise geometries. The gate design, venting, and overall cavity configuration may need adjustments to compensate for the slower flow or cooling rates. In this context, moulds designed for traditional plastics may still be used with modification, but in some cases, dedicated tools for bio-based materials may offer better results.
Mechanical compatibility also extends to the wear and abrasion effects that biodegradable plastics can impose on the mould. Some bio-compounds are filled with natural fibers, which can be more abrasive than pure resins. This introduces the possibility of accelerated mould wear, especially if softer tool steels are used. High-performance alloys or surface treatments like PVD coating may be required to extend tool life and maintain surface finish quality. Manufacturers must weigh these requirements against production volumes and cost considerations when deciding whether to adapt existing moulds or invest in new ones.
Moreover, the environmental benefits of biodegradable plastics may only be fully realized if the production process itself remains energy efficient and waste-reducing. This places a premium on moulds that enable fast cycle times, reduced scrap rates, and rework. Some legacy Children Toy Mould configurations may struggle in this regard if they were not originally optimized for modern efficiency standards. Integrating advanced cooling systems, automation, and real-time monitoring can help bridge this gap and bring legacy tools up to speed.
Finally, regulatory and safety standards for children's toys also play a role. Any material used in conjunction with toy moulds must be compliant with international health and safety regulations. Biodegradable plastics are still undergoing evaluation for durability, allergenicity, and toxin release under various use conditions. Therefore, the interaction between moulded part design, material formulation, and the capabilities of the tooling system must be holistically addressed to ensure compliance.
While traditional mould systems can be adapted to process biodegradable plastics, doing so effectively requires careful attention to material behavior, thermal control, wear resistance, and process efficiency. With appropriate modifications, Children Toy Mould can remain highly relevant and useful in a market increasingly driven by sustainability and environmental innovation. The future of toy manufacturing will likely see a blend of material science advancements and tooling evolution, opening new doors for eco-conscious product design.




 Search...
Search... English
English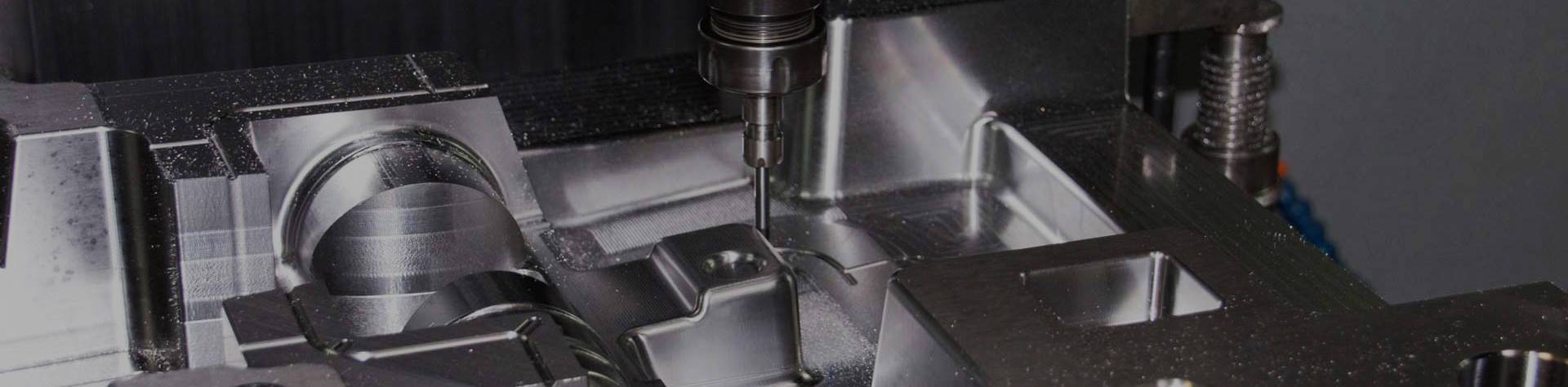



.jpg)
.jpg)
