Optimizing Runner Systems in Basket Mould Injection Processes
Understanding the Role of Runners in Basket Moulds
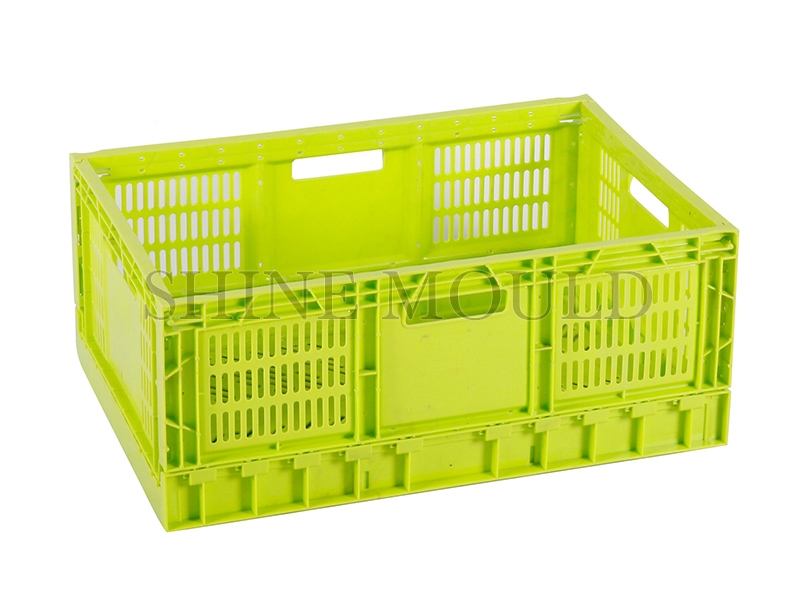
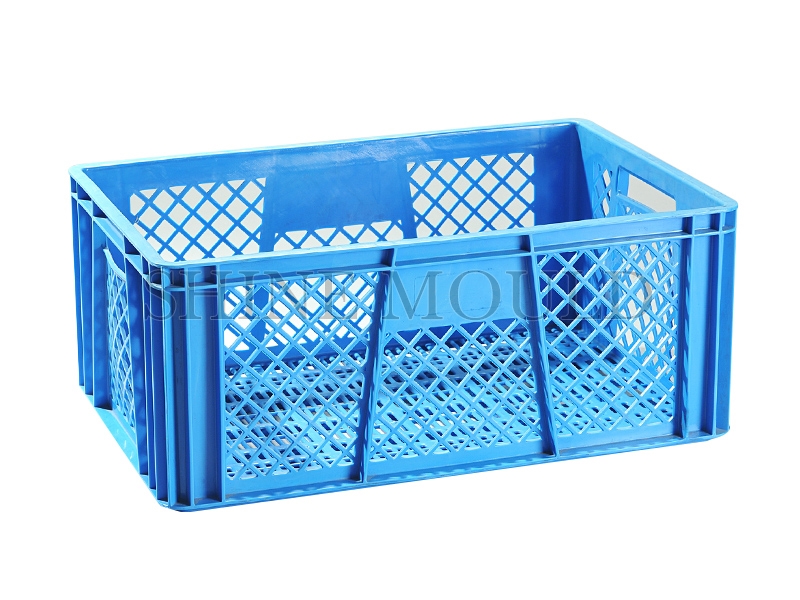
In the production of plastic baskets, such as shopping baskets, laundry baskets, and storage containers, the design of the runner system plays a crucial role in determining product quality and manufacturing efficiency. Runners are channels that guide molten plastic from the injection unit to the cavities of the mould. Poorly designed runners can cause uneven filling, warping, surface defects, or extended cycle times. For Basket Moulds, especially those with multiple cavities, achieving uniform flow is essential to ensure consistent wall thickness and structural integrity across all products.

Cold Runners vs. Hot Runners
One of the fundamental considerations in Basket Mould design is choosing between cold and hot runner systems. Cold runners are simpler and less expensive, making them suitable for small to medium-sized batches or for materials that are prone to degradation at high temperatures. However, they generate more waste because the runner solidifies along with the part and must be trimmed after ejection. In contrast, hot runners maintain the plastic in a molten state, reducing waste and cycle times. Hot runner systems are often preferred for high-volume production of shopping and storage baskets, as they can improve efficiency while maintaining consistent quality.
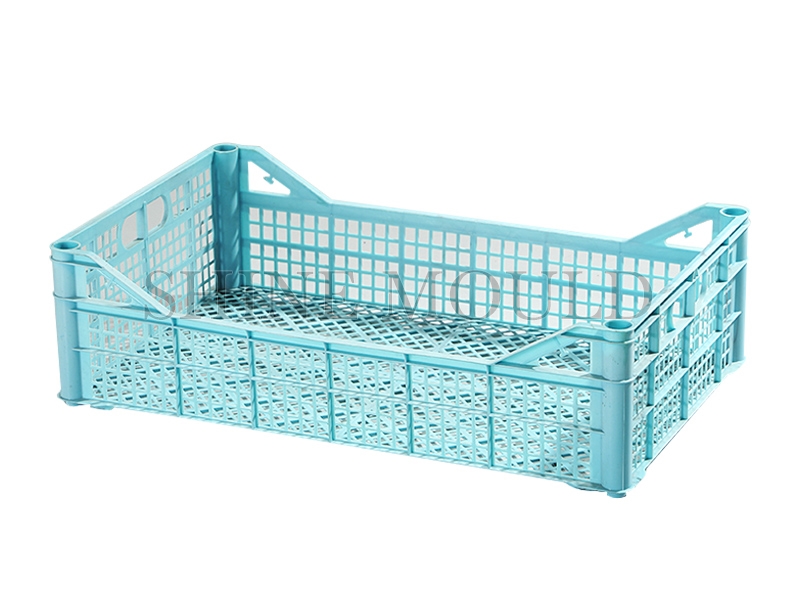
Design Considerations for Shopping Baskets
Shopping baskets typically have complex geometries with open grids or reinforced edges. For these parts, a Basket Mould should incorporate runners that decrease pressure drop while promoting balanced flow. It is essential to strategically locate gates, typically at the thicker structural areas, to prevent sink marks and ensure proper filling of thin-walled sections. Cold runners can be used for simpler designs, but in high-volume production, hot runners help maintain dimensional accuracy and reduce post-processing.
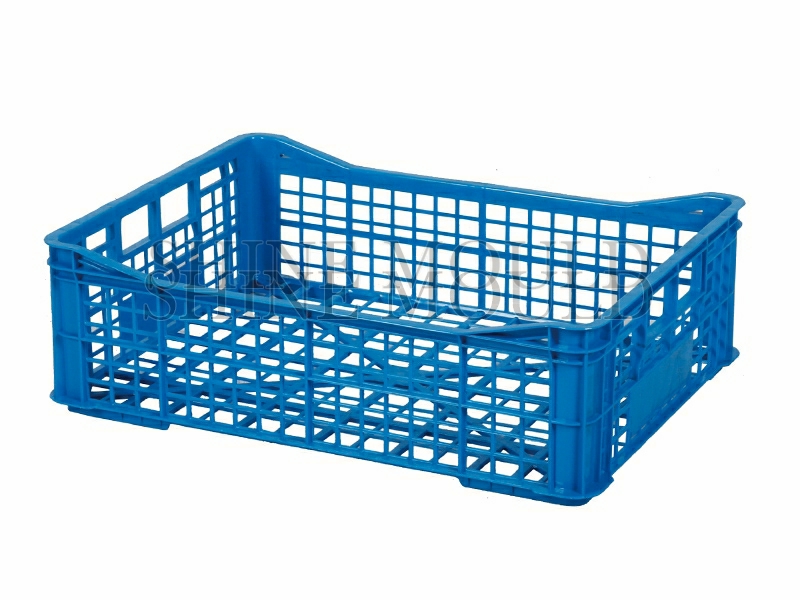
Optimizing Laundry Basket Moulds
Laundry baskets often feature perforated or lattice surfaces to facilitate airflow. The runner system must allow the molten plastic to reach all thin sections without freezing prematurely. Cold runner designs must be short and well-insulated, whereas hot runners can deliver molten material directly to each cavity without creating weld lines that could weaken the structure. Proper gate placement, combined with a careful balance of runner diameter and flow length, ensures uniform filling and reduces the risk of warpage during cooling.
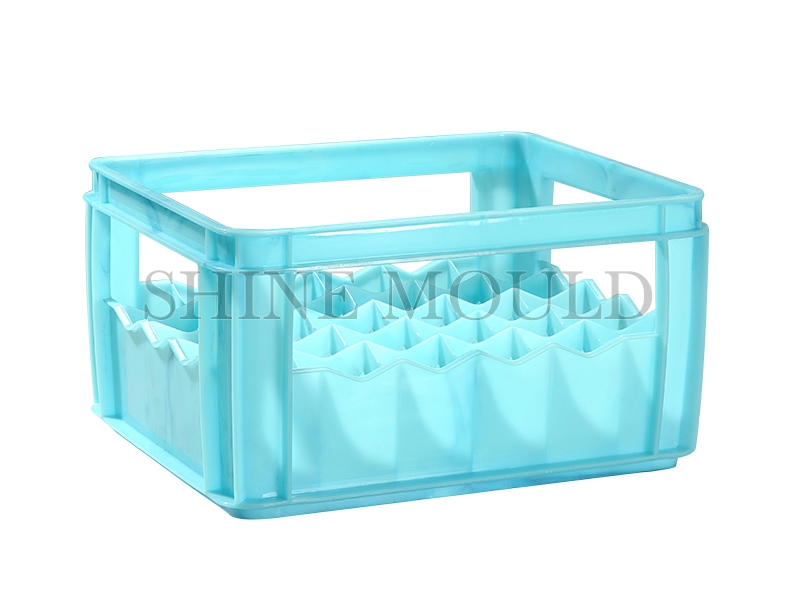
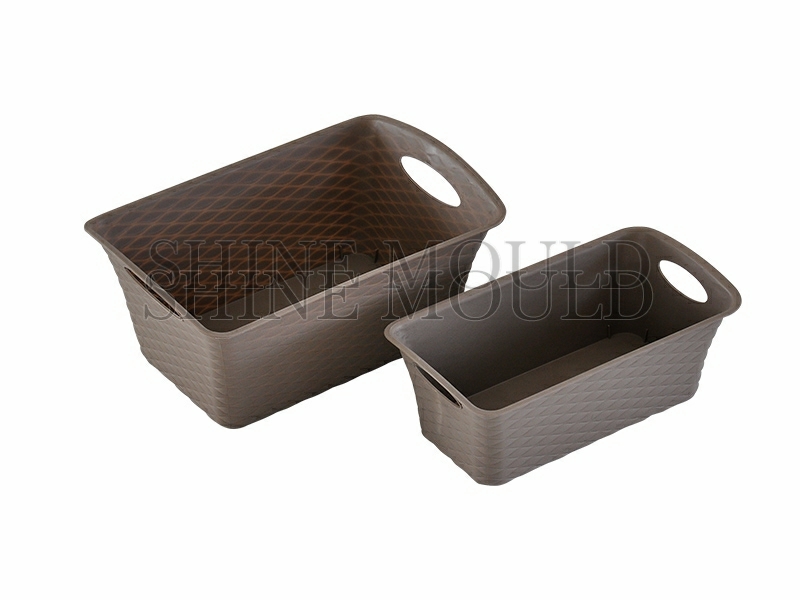
Storage Basket Production Requirements
Storage baskets vary widely in size and complexity, sometimes incorporating handles or interlocking features. For such designs, a Basket Mould should provide sufficient thermal control in the runner system. Hot runner systems offer better control for larger or multi-cavity moulds, ensuring that all cavities receive material at similar temperatures. Designers must also consider venting and gate location to prevent air traps, which could affect structural integrity or surface finish.
Balancing Cost, Efficiency, and Quality
Ultimately, designing cold or hot runners in Basket Moulds involves a balance between initial tooling cost, cycle efficiency, material waste, and product quality. While hot runner systems are more expensive upfront, they reduce scrap and improve throughput for large-scale basket production. Cold runners remain a cost-effective choice for smaller batches or simpler designs. Engineers must evaluate the basket’s geometry, material type, and production volume to determine a suitable runner system.
Proper runner design is a key factor in producing high-quality shopping, laundry, and storage baskets. Whether employing cold or hot runners, designers of Basket Moulds must carefully consider gate placement, flow balance, and thermal management. A well-optimized runner system not only enhances product consistency but also improves manufacturing efficiency and reduces production costs, making it a critical aspect of modern injection moulding practices.




 Search...
Search... English
English